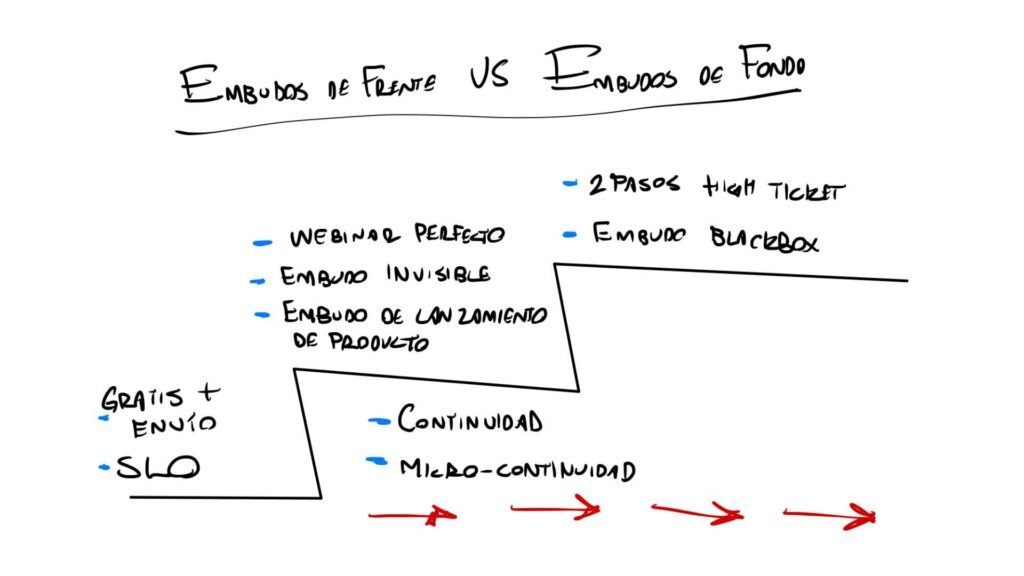
Russell Brunson uses the terms "Frontend Funnels" and "Backend Funnels" to describe two crucial phases in the sales and marketing strategy within a business. Understanding the difference between these two types of funnels is essential to maximizing conversions and customer value over time.
Frontend Funnels (frontend funnels)
Objective: Acquire new customers.
Front-end funnels are designed to attract cold traffic and convert visitors into first-time customers. These funnels usually start with a low-cost or even free offer, such as a free product plus shipping or a self-checkout (SLO) funnel. The main goal is to get prospects to take that first step of engagement by buying something small, allowing them to get to know and trust your brand.
Characteristics:
- Low-cost or free offers.
- Focus on converting cold traffic into paying customers.
- Lead generation through squeeze pages, pop-ups, or free trials.
Backend Funnels (backend funnels)
Objective: Maximize customer value.
Backend funnels are used to scale and nurture customers who have already purchased something from you, i.e. warm traffic. These funnels are designed to offer higher value products and build long-term relationships. As customers move up the value ladder, backend funnels can include upsells, cross-sells and high-ticket offers.
Characteristics:
- Higher value offers.
- Focus on converting current customers into repeat and loyal customers.
- Use of complex and customized sales funnels, such as webinars, memberships, and advanced programs.
Continuity of Product Knowledge
How you talk to your potential customers depends on where they are in their product awareness journey.
Cold traffic is probably only aware of the problem they face; they don't know you or your product. Start the value ladder at the lowest level, such as a free product plus shipping or a self-checkout funnel (SLO).
Step 1: Landing Page
These funnels start at the landing page. They do not cover the temperature of the traffic or the pre-frame bridge. They are the sales mechanisms designed to move a person from being a completely anonymous visitor to becoming a paying customer. Traffic and pre-frame are also important elements, so be sure to consider them carefully when deciding which funnel to use.
Step 2: Nurture and Scale
When you're ready to "nurture and scale" customers on your value ladder, all you have to do is create a new funnel. The people you nurture and scale will now be considered warm traffic, so you can treat them like old friends and approach them with funnels from that perspective.
Step 3: Funnels and Scripts
Some of these funnels and scripts are short and concise. Some are very long and involved. In general, the higher up the value ladder you are, the more sales you will have to make and the longer your script will be. Although, if you have hot traffic, sometimes you can simplify the script and still get good results.
The Big Picture
This is how Russell sees companies when he first starts working with them. After seeing what a business looks like from this high-level view, he can easily see what's broken and then dive into the details to get the results owners want and need.
I encourage you to take what you have learned so far, along with what you are currently doing in your business. Determine what you need to change or create to build your solid foundation.
Conclusion
The key to moving up the value ladder is to understand the temperature of your traffic and tailor your funnels and messaging accordingly. From cold traffic that barely knows you to warm traffic that already trusts you, each step requires a specific and careful approach. Use these principles to build effective funnels that guide your customers through each stage of their journey, from initial awareness to becoming loyal, repeat customers.